Investors often seek high-yield investments to generate steady income, particularly in low-interest-rate environments. While high-yield investments can offer attractive returns, they often come with higher risks. This article will explore what high-yield investments are, how to calculate dividend yield for individual stocks and a portfolio, the types of investments that typically offer high yields, and provide examples of high-yield dividend stocks.
What is Dividend Yield?
Dividend Yield is a financial ratio that indicates how much a company pays out in dividends relative to its stock price. It’s a measure of the income generated by an investment, expressed as a percentage of the current stock price.
How to Calculate Dividend Yield
The formula for calculating dividend yield is:
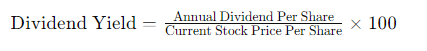
Example:
Suppose a company pays an annual dividend of $2 per share, and its current stock price is $50. The dividend yield would be:
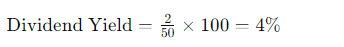
This means the company offers a 4% yield, providing an income return of 4% of your investment annually through dividends.
How to Calculate Dividend Yield for an Overall Portfolio
Calculating the dividend yield for an entire portfolio requires considering the dividend yields and values of all individual investments.
Steps to Calculate Portfolio Dividend Yield:
- Determine the Dividend Yield of Each Stock:
- Use the dividend yield formula for each stock in your portfolio.
- Find the Value of Each Investment:
- Calculate the market value of each investment by multiplying the number of shares by the current stock price.
- Calculate the Total Value of the Portfolio:
- Sum up the market values of all investments in your portfolio.
- Calculate the Weighted Dividend Yield for Each Investment:
- Multiply the dividend yield of each stock by the proportion of that stock’s value relative to the total portfolio value: Weighted Dividend Yield=Individual Stock Dividend Yield×(Value of the InvestmentTotal Portfolio Value)\text{Weighted Dividend Yield} = \text{Individual Stock Dividend Yield} \times \left(\frac{\text{Value of the Investment}}{\text{Total Portfolio Value}}\right)Weighted Dividend Yield=Individual Stock Dividend Yield×(Total Portfolio ValueValue of the Investment)
- Sum the Weighted Dividend Yields:
- Add up the weighted dividend yields to get the overall portfolio dividend yield.
Example:
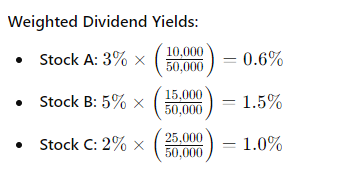
Assume your portfolio consists of:
- Stock A:
- Dividend Yield: 3%
- Value: $10,000
- Stock B:
- Dividend Yield: 5%
- Value: $15,000
- Stock C:
- Dividend Yield: 2%
- Value: $25,000
Total Portfolio Value: $50,000
Portfolio Dividend Yield:
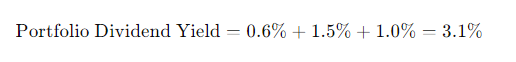
This 3.1% represents the overall dividend yield of your portfolio.
Types of Investments That Typically Have High Yields
High-yield investments provide higher income returns but may come with increased risk. Here are some common types:
- High-Yield Bonds (Junk Bonds):
- Description: Bonds issued by companies with lower credit ratings, offering higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk of default.
- Risk: Higher default risk compared to investment-grade bonds.
- Dividend Stocks (High-Yield or Income Stocks):
- Description: Stocks of companies that pay high dividends, often found in mature industries like utilities, real estate, or telecommunications.
- Risk: Potentially limited capital appreciation and risk of dividend cuts if the company faces financial challenges.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs):
- Description: Companies that own and operate income-producing real estate. Required by law to pay out most earnings as dividends.
- Risk: Sensitive to interest rates and economic cycles affecting property values and rental income.
- Master Limited Partnerships (MLPs):
- Description: Typically found in the energy sector, MLPs pay out a significant portion of cash flow as distributions.
- Risk: Commodity price sensitivity and regulatory risks can affect performance.
- Preferred Stocks:
- Description: A type of equity with fixed dividends, often higher than common stocks.
- Risk: Less upside potential and sensitivity to interest rate changes.
- Business Development Companies (BDCs):
- Description: BDCs invest in small and mid-sized businesses, offering high dividends.
- Risk: Volatility due to the riskier nature of the companies they invest in.
- Emerging Market Bonds:
- Description: Bonds issued by governments or corporations in emerging markets.
- Risk: Political, economic, and currency risks are higher.
- High-Yield Savings Accounts and CDs:
- Description: Low-risk, FDIC-insured options with relatively high yields compared to traditional accounts.
- Risk: Low risk but potentially lower returns that may not keep up with inflation.
- Closed-End Funds:
- Description: Pooled investment funds that often use leverage to enhance returns.
- Risk: Use of leverage can amplify losses, and these funds can trade at discounts or premiums to NAV.
- High-Yield ETFs and Mutual Funds:
- Description: Funds that invest in high-yield bonds, dividend stocks, or other income-producing assets.
- Risk: Varies based on underlying assets but generally higher risk than low-yield investments.
Examples of High-Yield Dividend Stocks
Here are some companies that have historically offered high dividend yields:
- AT&T Inc. (T)
- Sector: Telecommunications
- Dividend Yield: Around 7-8%
- Description: A major U.S. telecommunications company with stable cash flow and a long history of dividends.
- Verizon Communications Inc. (VZ)
- Sector: Telecommunications
- Dividend Yield: Around 6-7%
- Description: Another large telecommunications provider, offering strong dividend yields.
- Altria Group, Inc. (MO)
- Sector: Tobacco
- Dividend Yield: Around 8-9%
- Description: A leading tobacco producer with a high dividend yield, supported by strong pricing power.
- Philip Morris International Inc. (PM)
- Sector: Tobacco
- Dividend Yield: Around 5-6%
- Description: Known for the Marlboro brand, offering a strong dividend track record.
- Exxon Mobil Corporation (XOM)
- Sector: Energy (Oil & Gas)
- Dividend Yield: Around 3-4%
- Description: One of the largest energy companies, with a history of maintaining and increasing dividends.
- Chevron Corporation (CVX)
- Sector: Energy (Oil & Gas)
- Dividend Yield: Around 3-4%
- Description: A major player in the global energy sector, offering a solid dividend yield.
- Lumen Technologies Inc. (LUMN)
- Sector: Telecommunications
- Dividend Yield: Around 8-9%
- Description: Offers high-yield dividends but operates in a challenging sector.
- IBM Corporation (IBM)
- Sector: Information Technology
- Dividend Yield: Around 4-5%
- Description: A technology giant with a strong dividend history.
- AbbVie Inc. (ABBV)
- Sector: Pharmaceuticals
- Dividend Yield: Around 4-5%
- Description: Known for its blockbuster drug Humira, AbbVie is attractive for income-focused investors.
- Realty Income Corporation (O)
- Sector: Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT)
- Dividend Yield: Around 4-5%
- Description: Known as “The Monthly Dividend Company,” offering reliable dividends.
Conclusion
High-yield investments can be a powerful tool for generating income, but they come with risks that investors must carefully consider. Whether you’re investing in high-yield bonds, dividend stocks, REITs, or other income-producing assets, it’s essential to understand the trade-offs between yield and risk. Always conduct thorough research and consider diversifying your investments to mitigate potential risks.
Before investing, consult with a financial advisor to ensure that your investment choices align with your financial goals and risk tolerance. High yields can be attractive, but they should be part of a well-balanced portfolio strategy.
This comprehensive guide provides a strong foundation for understanding high-yield investments, helping investors make informed decisions to achieve their income and financial goals.
Related Articles:
- A Letter to My 20-Year-Old Self: Financial Wisdom for a Secure Future
- Invest $50 Weekly in VOO: Higher Returns Than Lattes
Financial Disclaimer
The information provided on HelpyYourFinances.com is for general informational purposes only and is not intended to be financial advice. While we strive to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the content, it is important to remember that financial decisions are personal and should be tailored to your individual circumstances.
We strongly recommend that you consult with a qualified financial advisor or other professional before making any financial decisions. The content on this website should not be considered a substitute for professional financial advice, analysis, or recommendations. Any reliance you place on the information provided is strictly at your own risk.



